CBCT Imaging and Root Canal Treatment for Taurodontism in Mandibular Second Molar - A Case Report and Literature Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.v17i11.5212Abstract
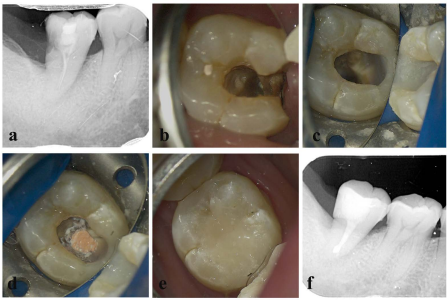
The mandibular second molar exhibits a wide range of intricate root canal variations, which can present challenges and difficulties in achieving successful root canal treatment. This report focuses on two specific cases involving a root canal variation in a typical taurodontism of the mandibular second molar. To provide a comprehensive analysis and illustration of the anatomical structure of intraoral taurodontism and the important considerations for root canal treatment, we utilized advanced imaging techniques such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and a dental microscope. By combining these tools, we were able to gain a deeper understanding of the complex root canal system and make informed decisions during the treatment process.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





