Diagnosis and Endovascular Treatment of Coronary Artery Fistula: A Case of symptomatic Left-to-Right shunt
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.5637Abstract
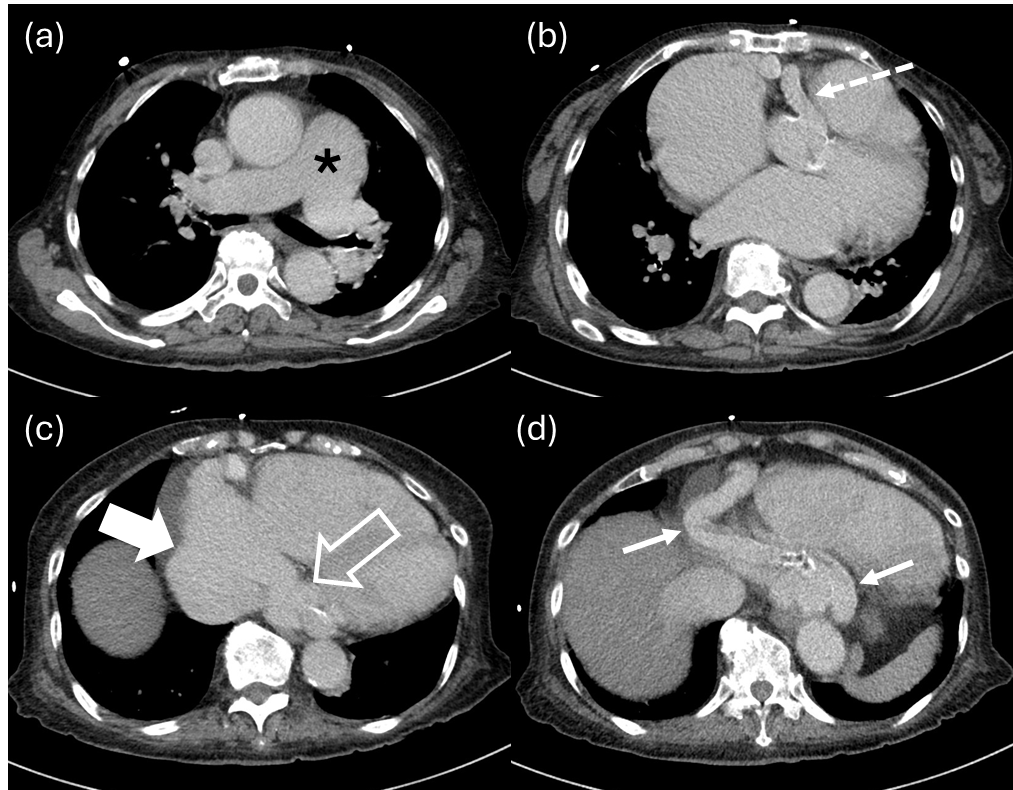
Coronary artery fistulas (CAFs) are rare vascular malformations which constitute abnormal communications from coronary arteries to cardiac chambers, or to parts of the systemic or pulmonary circulation. While small CAFs are usually asymptomatic and often resolve spontaneously, medium or large CAFs can result in haemodynamically significant shunting with progressive dilation. We report a case of CAF originating from the right coronary artery and draining into the coronary sinus, which resulted in pulmonary hypertension and heart failure. The patient subsequently underwent percutaneous flow retardation with vascular plug and coils, leading to significant reduction of shunt flow and clinical improvement. CT and procedural fluoroscopic images are provided.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





