Extra-Articular Localized Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor of the Deep Infrapatellar Bursa
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.5568Abstract
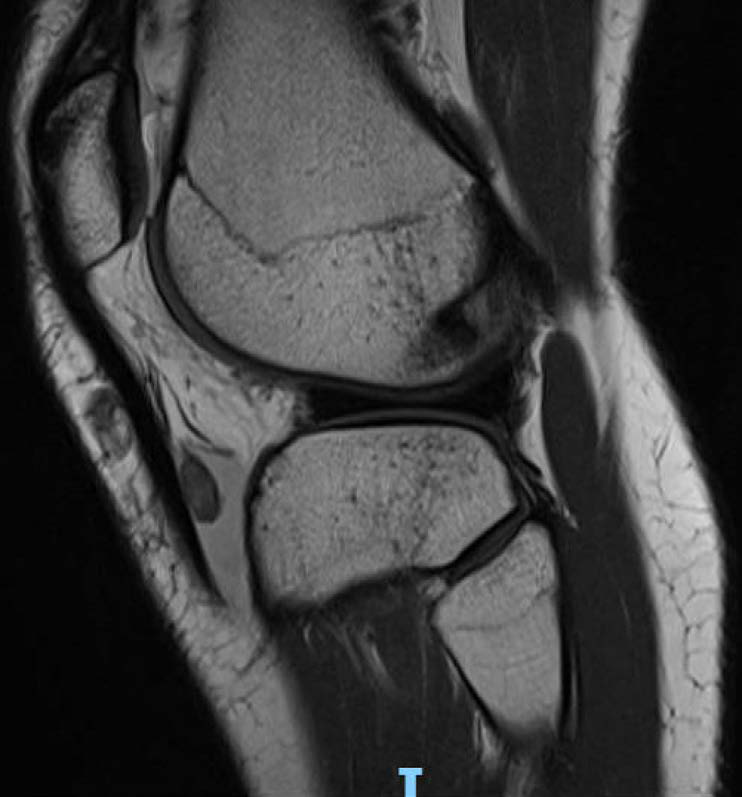
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT), previously called pigmented villonodular tenosynovitis (PVNS) or giant cell tumor of tendon sheath, is a rare mesenchymal neoplasm arising from the synovium of joints and tendon sheaths. This condition has insidious and nonspecific symptoms making its diagnosis challenging. In most cases, localized tenosynovial giant cell tumors are described in the hand and are infrequent in larger joints. In the rare cases that affect the knee, the most common location is Hoffa’s fat pad, followed by the suprapatellar bursa and the posterior capsule. Here, we describe a case of a histopathologically proven TGCT of the knee, found in an unusual location in the deep infrapatellar bursa, which was diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





