Case Report: Organo-axial Sigmoid Volvulus mimicking Sigmoid Colon Malignancy
-
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.5514Abstract
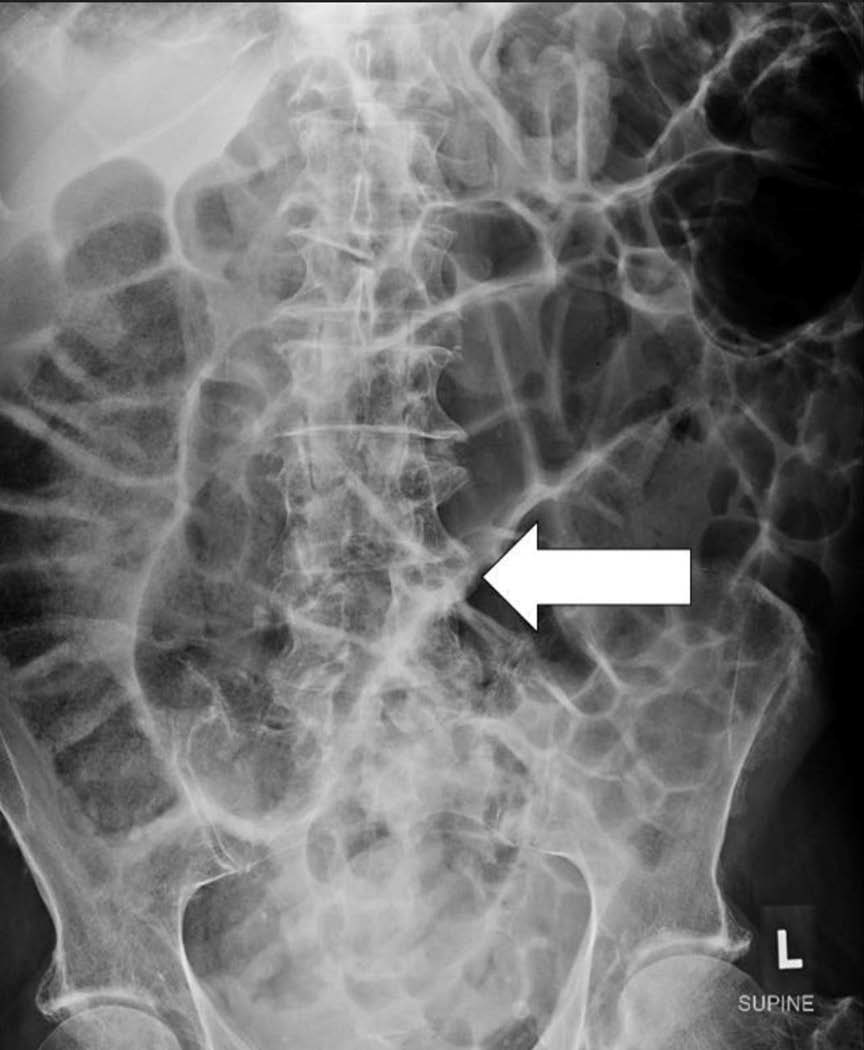
An 86-year-old man presented with 5 days of constipation and no constitutional symptoms. Despite a history of prior lower abdominal pain and constipation three months earlier, prior imaging and endoscopy revealed no suspicious findings. On admission, abdominal examination showed distension without tenderness, and initial laboratory results were unremarkable. Radiographs demonstrated dilated large bowel loops, while a follow-up CT scan revealed a transition point in the sigmoid colon with gross mural thickening of the sigmoid colon and whirling of the peri-colonic vessels along the long-axis of the sigmoid colon, leading to a diagnosis of organo-axial sigmoid volvulus. The patient’s symptoms resolved spontaneously during admission, and he was discharged after three days of conservative management.
Sigmoid volvulus is the most common colonic volvulus, occurring primarily in immobile, constipated individuals. Organo-axial volvulus, a rarer subtype, involves twisting along the longitudinal axis. Diagnosis is largely radiological, and early intervention is crucial to prevent complications such as bowel ischemia, necrosis, and perforation. While elective surgery is recommended to reduce recurrence and improve outcomes, conservative management may be suitable for frail, high-risk patients. Organo-axial volvulus should be considered in the differential diagnosis of sigmoid colon obstruction, especially when malignancy is suspected.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





