Management Interventions for Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia with Complications of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations and Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.5308Abstract
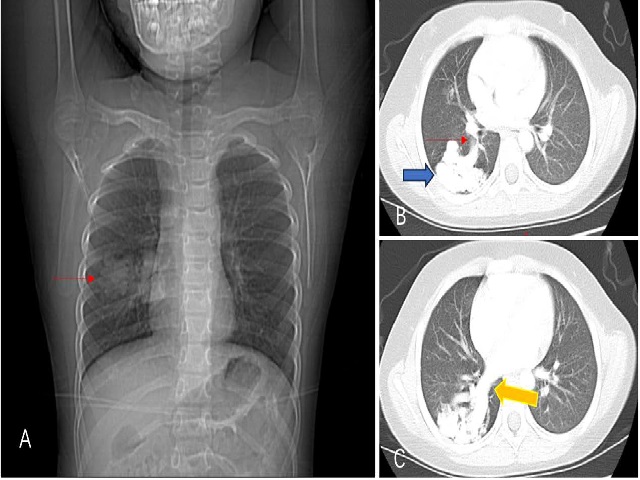
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the presence of vascular abnormalities that impact many organ systems. We present a case of a 6-year-old child diagnosed with HHT, who has experienced repeated epistaxis and had a family history of the condition. The patient complained of hypoxemia and seizures, Chest CT and cranial MRI confirmed the presence of both pulmonary and cerebral arteriovenous fistulas. A genetic test indicated an ENG gene mutation, which led to the diagnosis of HHT type I. Both the pulmonary and intracranial arteriovenous fistulas were embolized through intervention. The pulmonary arteriovenous fistula was treated by embolizing it with a spring coil, which effectively blocked the venous sac and the feeding arteries. As a result of the embolization, the child's hypoxemia totally resolved and returned to normal. The intracranial arteriovenous fistula was treated by embolization using a double microcatheter technique with spring coil along with Onyx. There were no complications such as cerebral hemorrhage or cerebral infarction following the embolization procedure, and there was no recurrence of seizures. Our case demonstrates that interventional embolization is an effective treatment for pulmonary and cerebral vascular abnormalities in symptomatic HHT.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





