Preoperative Transcatheter Arterial Embolization for Spontaneous Rupture of Huge Amebic Liver Abscess with Massive Intraperitoneal Hemorrhage
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.v17i8.4837Keywords:
Ruptured Amebic Liver Abscess, Active Hemorrhage, Computed Tomography, Digital Subtraction Angiography, Transcatheter Arterial Embolization, Liver, ParasiteAbstract
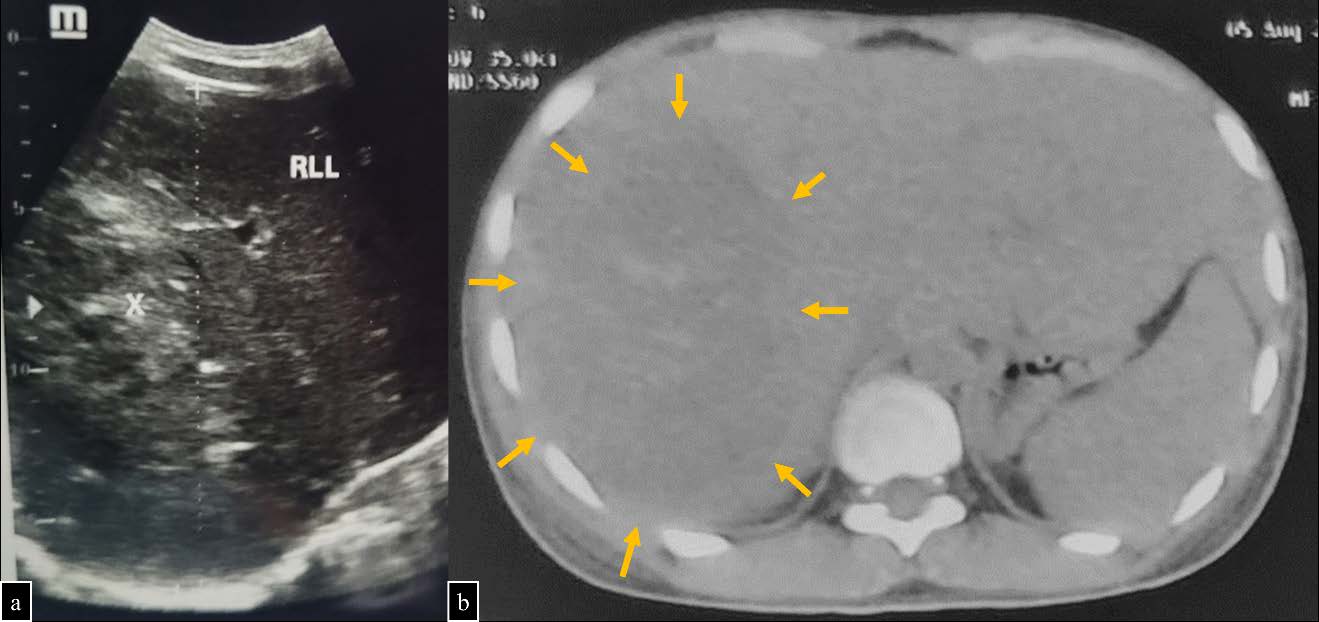
An 18-year-old male developed a huge liver abscess with severe anemia over the course of 2 weeks. Abdominal contrast enhanced computed tomography showed ruptured huge liver abscess in the right liver lobe with signs of active hemorrhage (contrast extravasation). Serology examination confirmed amoeba as the suspected pathogen of cause. Angiography was performed followed by transcatheter arterial embolization to localize and control the hemorrhage. Embolization using a combination of polyvinyl alcohol and gelfoam successfully controlled the active hemorrhage. Exploratory laparotomy was performed to evacuate and debride the huge abscess. Metronidazole was given and showed good results. Huge liver abscess size is a predictor of conservative management failure and requires a gradual step-up intervention. The purpose of this paper is to explain the importance of imaging in detecting liver abscess and active hemorrhage along with the role of interventional radiology in this case.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Radiology Case Reports

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The publisher holds the copyright to the published articles and contents. However, the articles in this journal are open-access articles distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License, which permits reproduction and distribution, provided the original work is properly cited. The publisher and author have the right to use the text, images and other multimedia contents from the submitted work for further usage in affiliated programs. Commercial use and derivative works are not permitted, unless explicitly allowed by the publisher.





